When using WordPress, you may notice that the “index.php” portion appears in the URLs of your website. This can be a hindrance to achieving cleaner, more user-friendly URLs. In this step-by-step guide, we will explain why “index.php” is showing in the URL and provide you with a solution to remove it, enhancing the overall appearance and SEO-friendliness of your WordPress site.
Step 1: Understanding why “index.php” appears in WordPress URLs
By default, the presence of “index.php” in WordPress URLs can be attributed to the way the WordPress Permalink settings are configured. This occurs when the “Plain” Permalink structure is selected, which uses query strings to display content.
Step 2: Accessing the WordPress Dashboard
To begin the process of removing “index.php” from WordPress URLs, access the WordPress Dashboard. Log in to your WordPress admin area using your credentials.
Step 3: Navigating to Permalink Settings
Once logged in, locate the “Settings” menu on the left-hand side of the Dashboard. Hover over it and click on “Permalinks.” This will take you to the Permalink Settings page.
Step 4: Choosing a Preferred Permalink Structure
On the Permalink Settings page, you will see various options for configuring your website’s permalinks. To remove “index.php” from your URLs, select a structure other than the default “Plain” setting. WordPress offers several options, including “Post name,” “Day and name,” and “Month and name.”
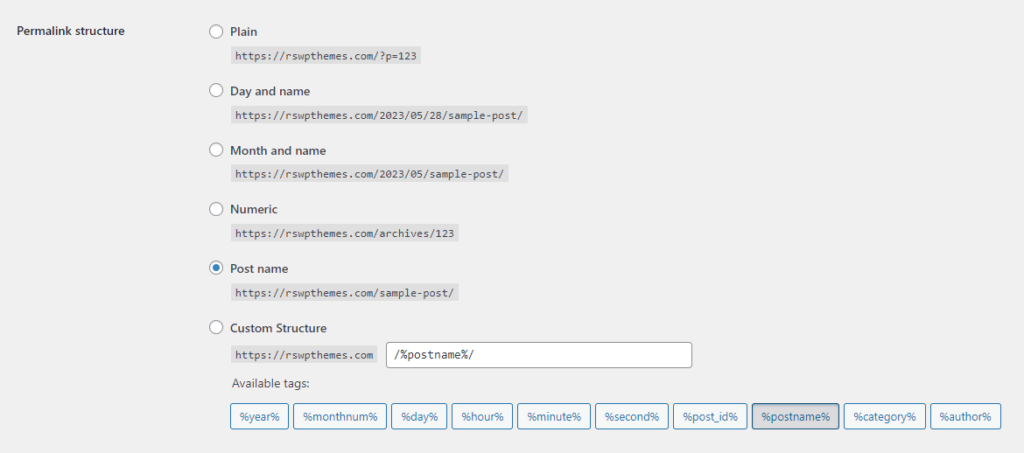
Step 5: Saving Changes
After selecting your desired Permalink structure, scroll down to the bottom of the page and click the “Save Changes” button. WordPress will then update the Permalink structure, removing “index.php” from your URLs.
Step 6: Updating the .htaccess file (Optional)
In some cases, removing “index.php” from your WordPress URLs may require an additional step. If you encounter any issues or your website displays a “404 Page Not Found” error after saving the Permalink changes, you may need to update your website’s .htaccess file.
6.1: Accessing the .htaccess file
Using an FTP client or cPanel file manager, navigate to the root folder of your WordPress installation. Look for the .htaccess file; it is usually located in the same directory as the “wp-content” folder.
6.2: Editing the .htaccess file
Right-click on the .htaccess file and choose the “Edit” or “Code Edit” option. Alternatively, you can download the file, edit it using a text editor, and re-upload it.
6.3: Adding code to remove “index.php”
Within the .htaccess file, add the following code snippet before any existing WordPress rules:
<IfModule mod_rewrite.c>
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteRule ^index\.php$ - [L]
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteRule . /index.php [L]
</IfModule>
6.4: Saving the .htaccess file
Save the changes made to the .htaccess file and upload it back to the root directory of your WordPress installation, replacing the existing file if prompted.
Step 7: Testing the URL Structure
To confirm that “index.php” has been successfully removed from your WordPress URLs, visit your website and navigate through its pages. Verify that the URLs are now clean and do not contain the “index.php” segment.
Conclusion
By following these step-by-step instructions, you should be able to remove “index.php” from your WordPress URLs. This will not only improve the aesthetics of your website’s links but also contribute to better search engine optimization (SEO) and user experience. Remember to regularly backup your .htaccess file and exercise caution while making any changes to ensure the smooth operation of your WordPress site.